We are composed of about thirty permanent and non-permanent staff. Our expertise is based on the constant development of innovative instrumentation and data analysis tools, and on the establishment or use of new theories and simulation tools. Our fields of application cover a variety of domains in materials science, nanooptics and biophysics, ranging from plasmonics to correlated oxides, through 2D materials physics, metallurgy or biomineralization.
Research highlights
-
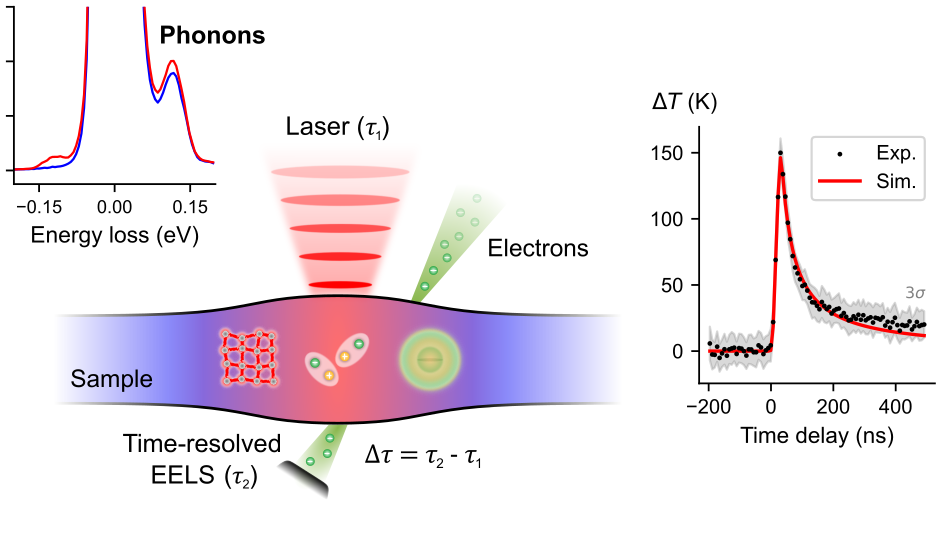
Nanosecond Nanothermometry in an Electron Microscope
Thermal transport in nanostructures plays a critical role in modern technologies. As devices shrink, techniques that can measure thermal properties at nanometer and nanosecond scales are increasingly needed to capture …
-
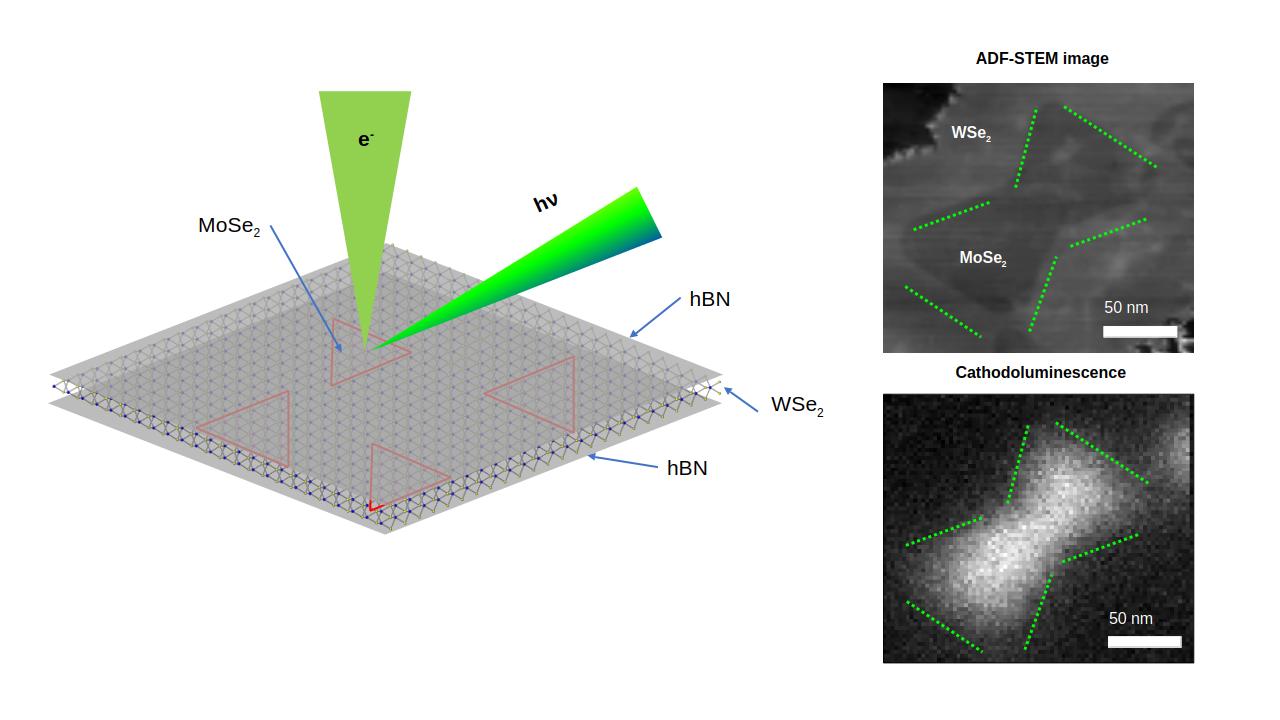
Quantum Confined Luminescence in Two Dimensions
2D materials, ANR, cathodoluminescence, Chromatem, EELS, nano-optics, van der Waals heterostructuresThe field of nanophotonics has witnessed a surge of interest in localized light emitters, driven by their potential to revolutionize optoelectronic devices. These emitters, including nanoparticles, nanowires, and quantum wells, …
-
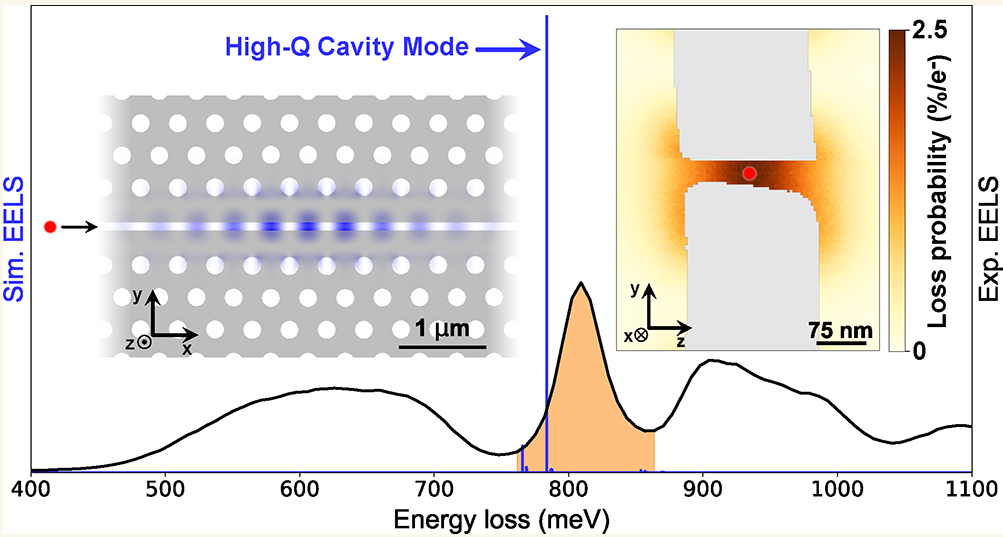
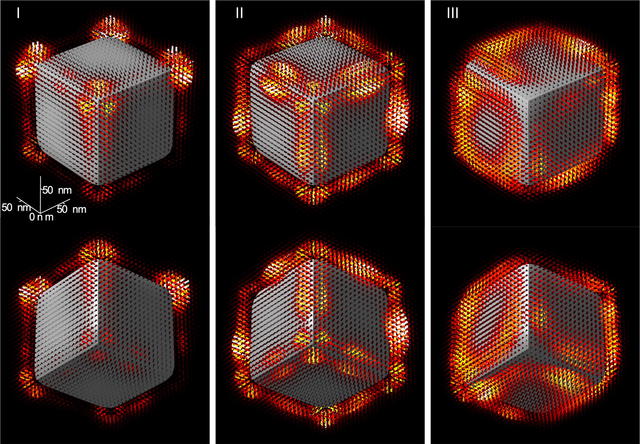
High-Efficiency Coupling of Free Electrons to Sub-wavelength cube Modal Volume, High‐Q Photonic Cavities
We report on the design, realization, and experimental investigation by spatially resolved monochro- mated electron energy loss spectroscopy (EELS) of high- quality-factor cavities with modal volumes smaller than λ3, with …
-
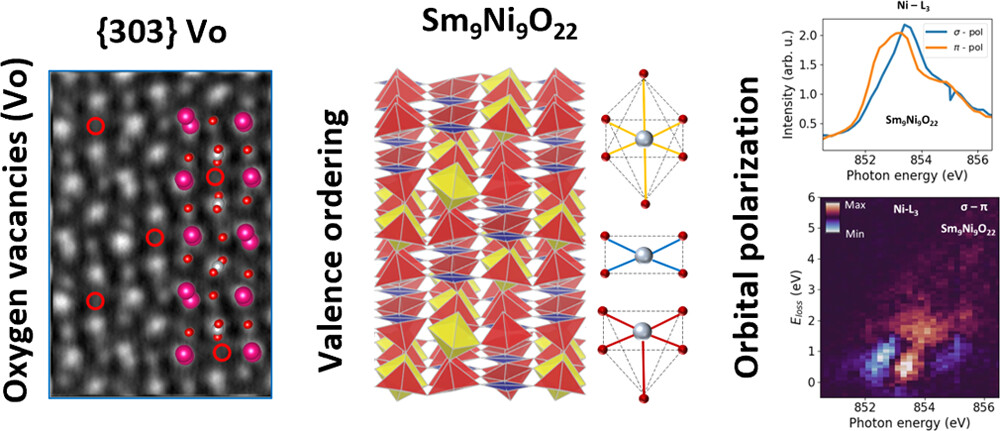
Valence-Ordered Thin-Film Nickelate with Tri-component Nickel Coordination Prepared by Topochemical Reduction
In a groundbreaking study, researchers have synthesized Sm9Ni9O22 using the metal-hydride-based “topochemical reduction” process. This compound exhibits ordered nickel valences associated with tri-component coordination configurations, resulting in a unique crystal …
-
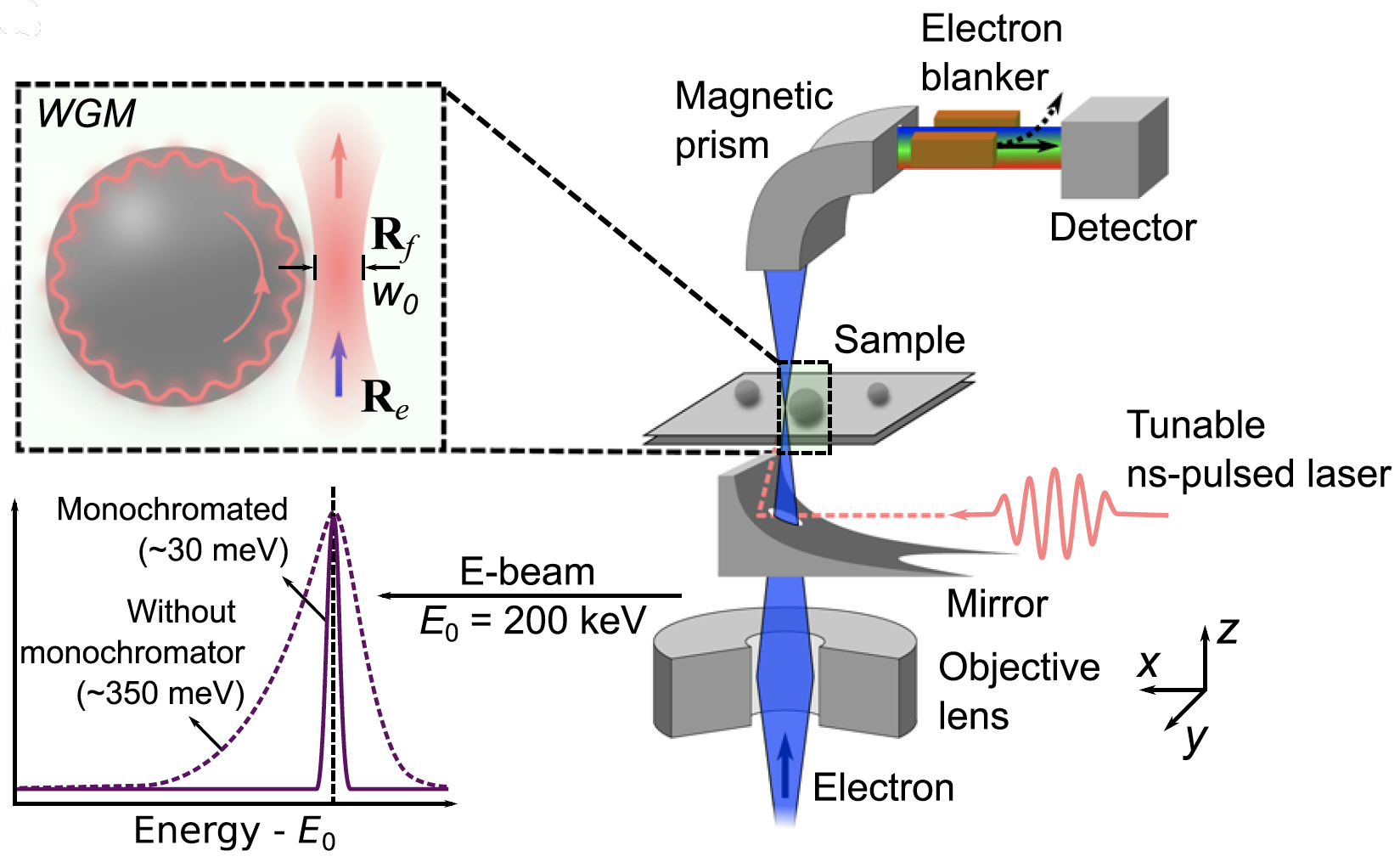
μeV electron spectromicroscopy using free-space light
The synergy between free electrons and light has recently been leveraged to reach an impressive degree of simultaneous spatial and spectral resolution, enabling applications in microscopy and quantum optics. However, …
-
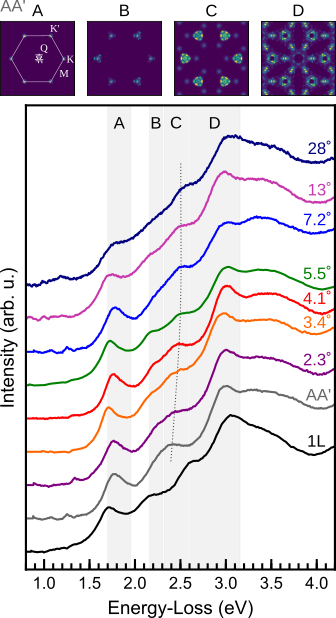
Excitonic absorption signatures of twisted bilayer WSe2 by electron energy-loss spectroscopy
Moiré twist angle underpins the interlayer interaction of excitons in twisted van der Waals hetero- and homostructures. The influence of twist angle on the excitonic absorption of twisted bilayer tungsten …
-
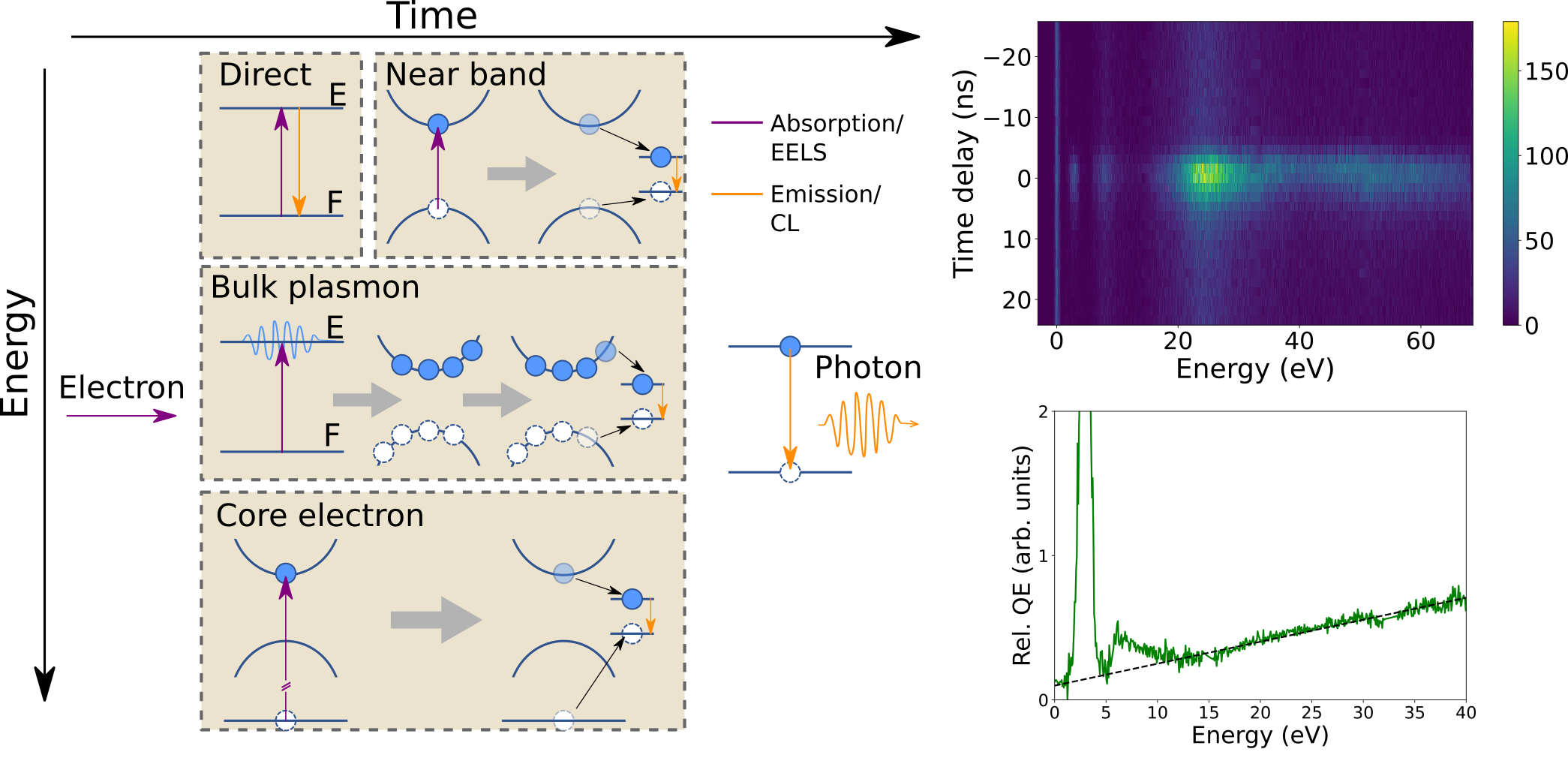
Cathodoluminescence excitation spectroscopy: Nanoscale imaging of excitation pathways
Following optical excitations’ life span from creation to decay into photons is crucial in understanding materials photophysics. Macroscopically, this is studied using optical techniques, such as photoluminescence excitation spectroscopy. However, …
-
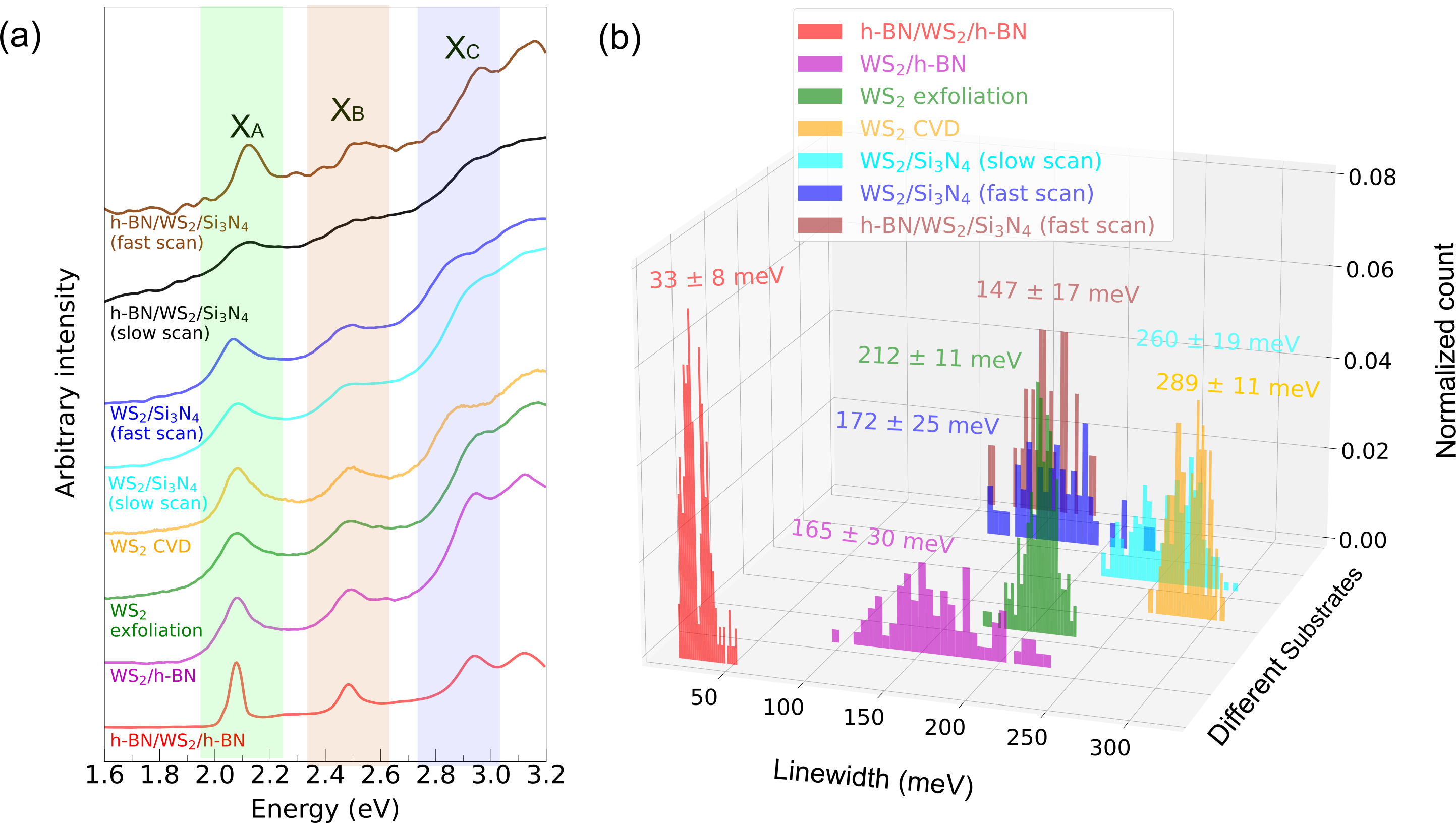
Substrate influence on transition metal dichalcogenide monolayer exciton absorption linewidth broadening
The excitonic states of transition metal dichalcogenide (TMD) monolayers are heavily influenced by their external dielectric environment and depend on the substrate used. In this work, various wide band gap …
-
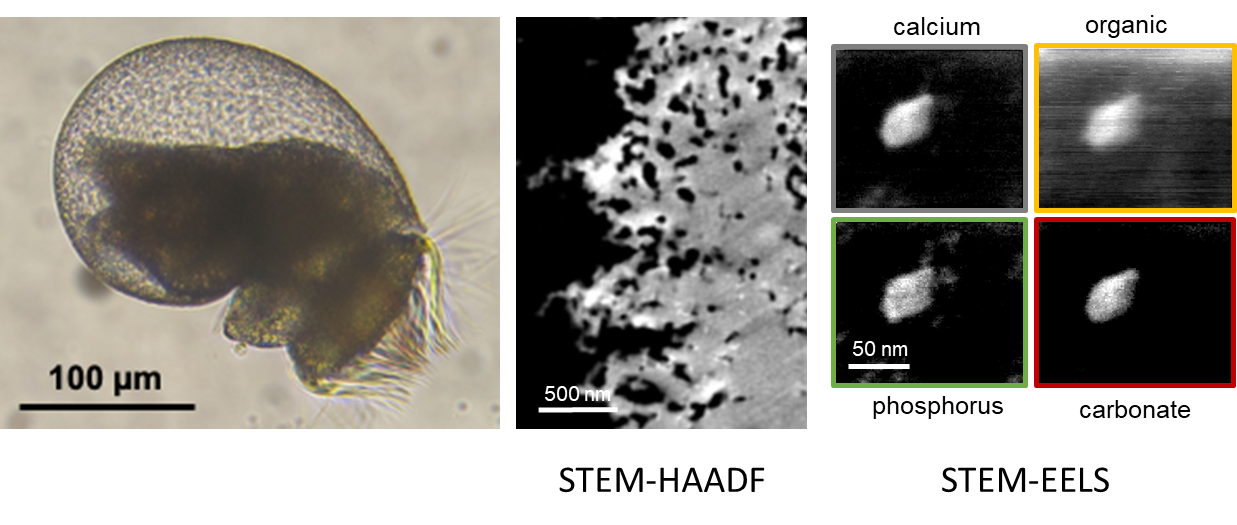
The abalone reveals its secrets about the origin of its shell
Many multicellular animals secrete a mineralized skeleton, a composite material in which the mineral phase, carbonated, phosphated or siliceous, is predominant. It is generally accepted that carbonates, which are abundant …
-
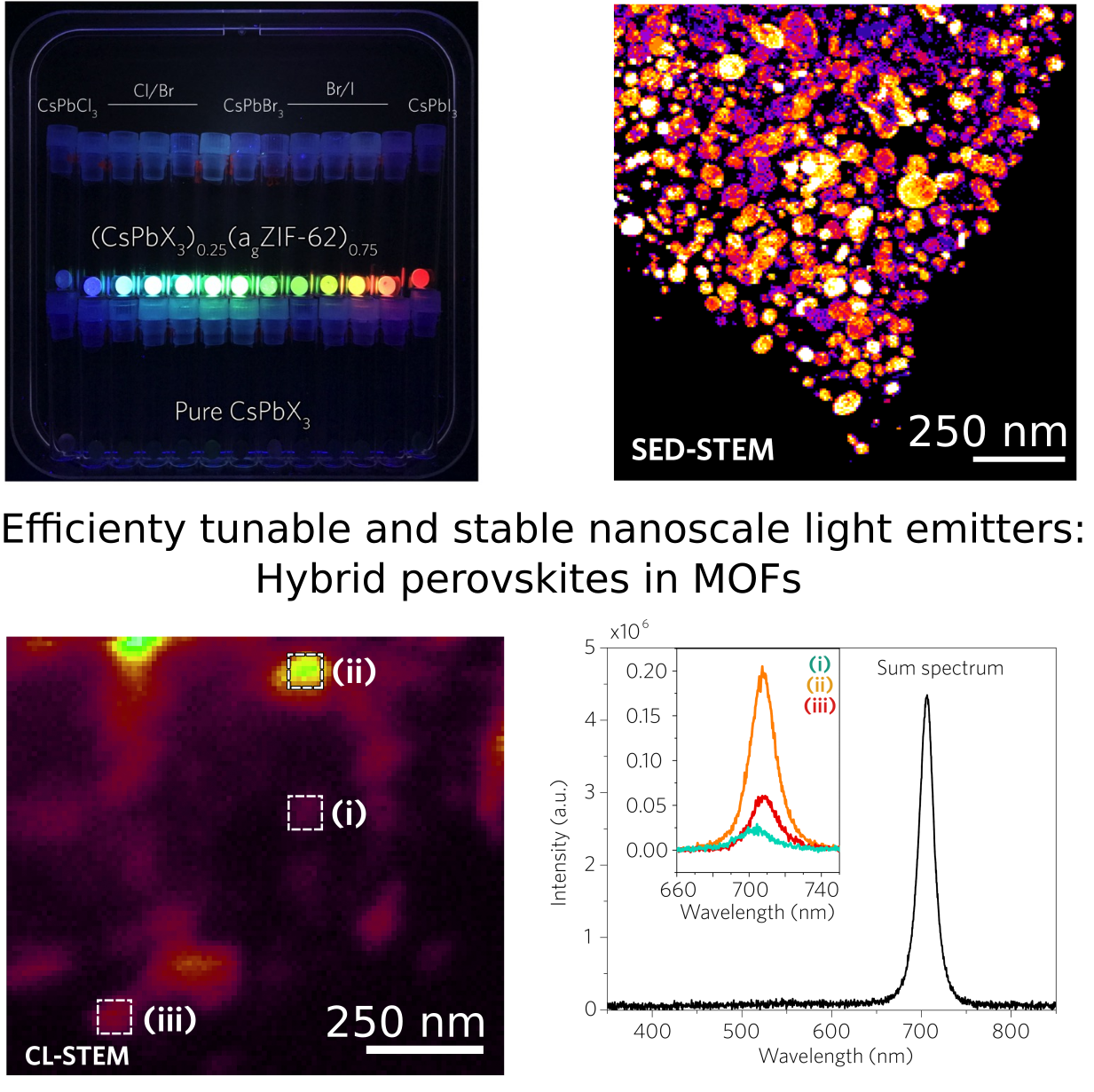
Liquid-phase sintering of lead halide perovskites and metal-organic framework glasses
Lead halide perovskite (LHP) semiconductors show exceptional optoelectronic properties. Barriers for their applications, however, lie in their polymorphism, instability to polar solvents, phase segregation, and susceptibility to the leaching of …
-
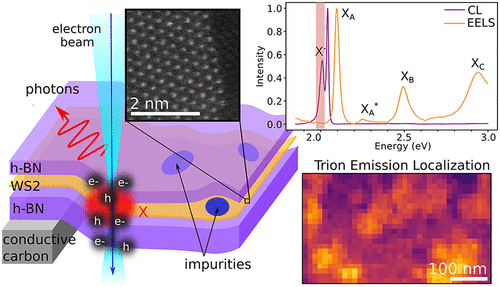
Nanoscale Modification of WS2 Trion Emission by Its Local Electromagnetic Environment
Structural, electronic, and chemical nanoscale modifications of transition metal dichalcogenide monolayers alter their optical properties. A key missing element for complete control is a direct spatial correlation of optical response …
-
Unveiling the Coupling of Single Metallic Nanoparticles to Whispering-Gallery Microcavities
Whispering-gallery mode resonators host multiple trapped narrow-band circulating optical resonances that find applications in quantum electrodynamics, optomechanics, and sensing. However, the spherical symmetry and low field leakage of dielectric microspheres …
-
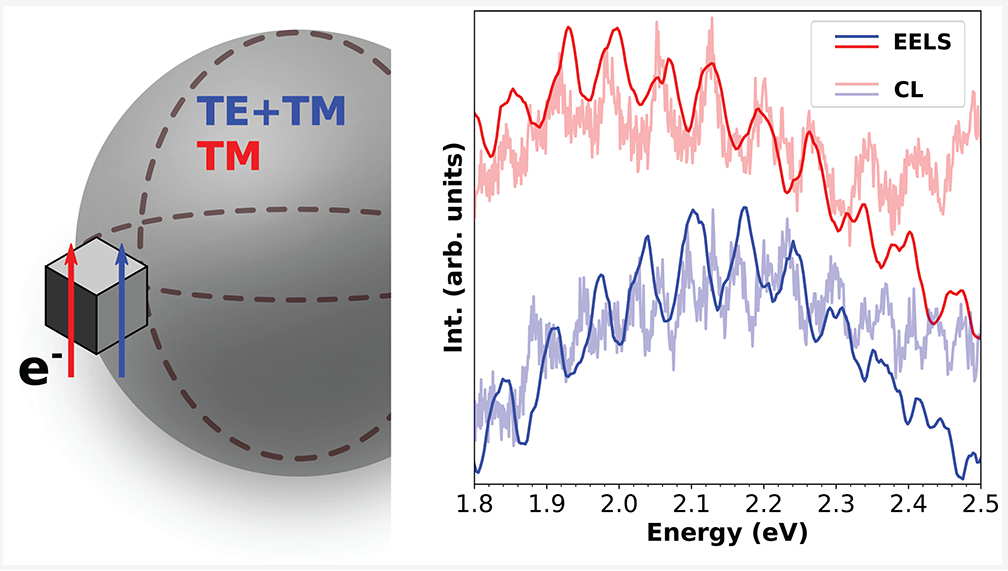
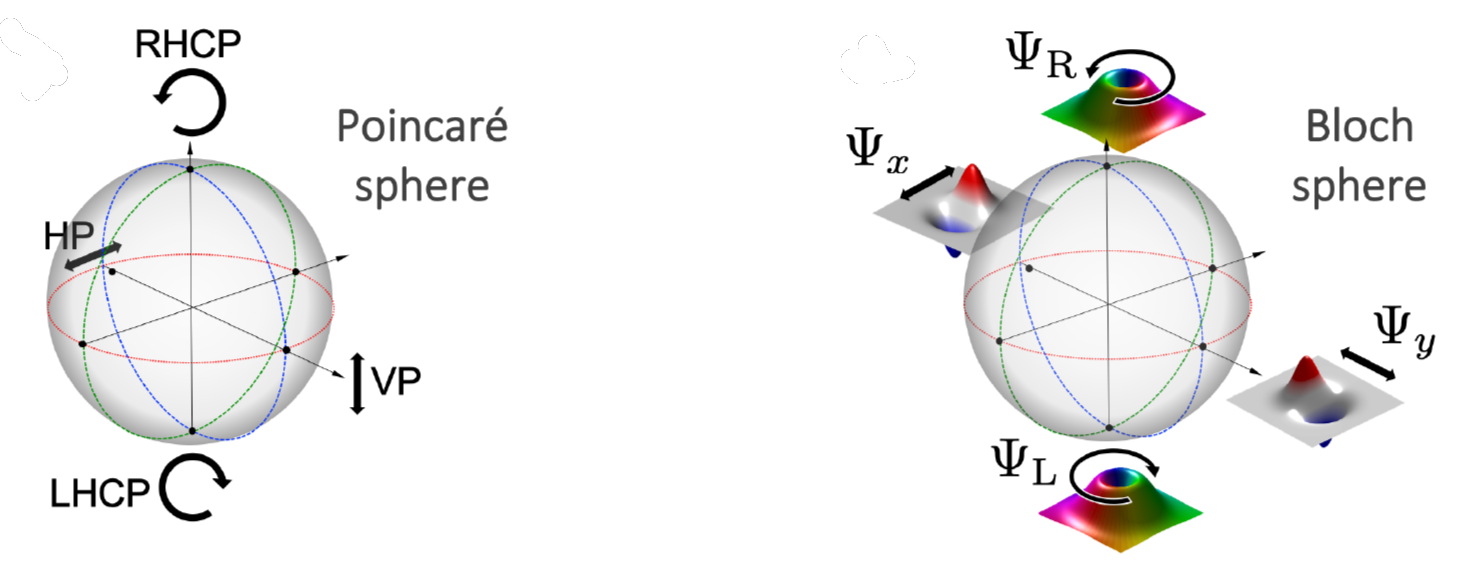
Optical polarization analogue in free electron beams
Spectromicroscopy techniques with fast electrons can quantitatively measure the optical response of excitations with unrivalled spatial resolution. However, owing to their inherently scalar nature, electron waves cannot access the polarization-related …
-
Three-dimensional vectorial imaging of surface phonon polaritons
Surface phonon polaritons (SPhPs) are coupled photon-phonon excitations that emerge at the surfaces of nanostructured materials. Although they strongly influence the optical and thermal behavior of nanomaterials, no technique has …
-
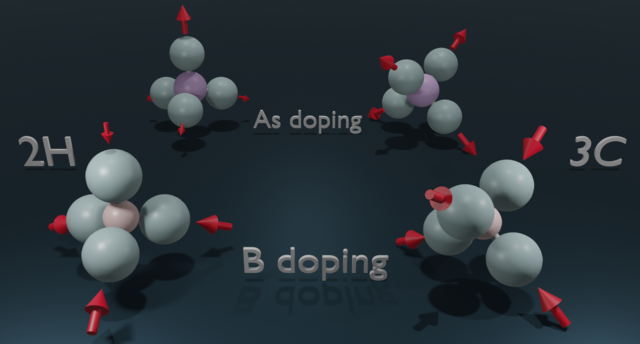
Extrinsic doping in group IV hexagonal-diamond-type crystals
Over the past few years, group IV hexagonal-diamond-type crystals have acquired a lot of attention in semiconductor physics thanks to the appearance of novel and very effective growth methods. However, …
-
Electronic structure and optical properties of semiconductor nanowires polytypes
Advances in the fabrication and characterization of nanowires polytypes have made crystal phase engineering a well-established tool to tailor material properties. In this review, recent progresses in the field are …
-
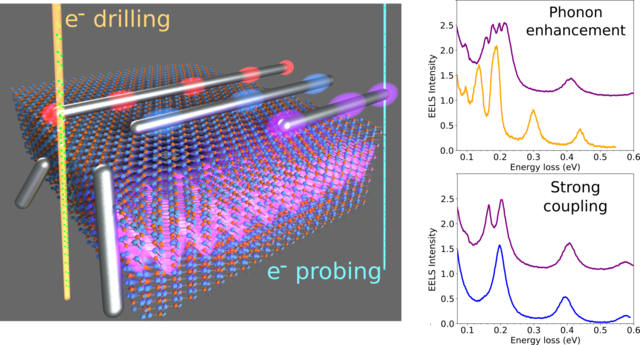
Tailored nanoscale plasmon-enhanced vibrational electron spectroscopy
Atomic vibrations and phonons are an excellent source of information on nanomaterials that we can access through a variety of methods including Raman Scattering, infrared spectroscopy, and electron energy-loss spectroscopy …